Share Post:
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, crucial for muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, mood regulation, libido, and overall vitality. While it naturally declines with age (about 1% per year after 30), it remains essential throughout life.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can help men with clinically low levels regain energy, libido, and muscle mass, but it comes with potential risks like cardiovascular issues, sleep apnea, and fertility reduction if misused or unmonitored.
Testosterone is not just about masculinity; it is a critical hormone for physical and mental health, but any supplementation should be medically supervised, individualized, and balanced with lifestyle changes.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Does Testosterone Do in the Body?
Function
Role in Male Health
Muscle Mass & Strength
Increases protein synthesis, muscle size, and recovery.
Bone Density
Supports bone mineralization, reducing osteoporosis risk.
Libido & Sexual Function
Maintains sex drive, erectile function, and sperm production.
Mood & Cognitive Function
Supports mood stability, memory, and focus.
Red Blood Cell Production
Stimulates erythropoiesis, reducing anemia risk.
Fat Distribution
Helps maintain lean mass, reduces visceral fat accumulation.
Expanded Explanation

Muscle Mass & Strength
Testosterone plays a direct role in increasing muscle protein synthesis, allowing men to build and maintain muscle mass more efficiently than women. This anabolic effect improves muscle size, strength, and recovery after exercise, which is why low testosterone often results in muscle weakness or noticeable loss of muscle mass, especially in the arms, legs, and chest.
Studies have shown that testosterone therapy in hypogonadal men can significantly increase lean muscle mass and decrease fat mass within 6–12 months of treatment, highlighting its critical role in body composition.
Bone Density
Testosterone is crucial for maintaining bone mineral density. It stimulates the activity of osteoblasts (bone-building cells) while reducing the activity of osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells), helping bones remain strong and reducing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
Low testosterone is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis in men, often overlooked until fractures occur. Research indicates that men with low testosterone levels are up to three times more likely to experience bone fractures compared to those with normal levels.
Libido & Sexual Function
What are the benefits of testosterone treatment in men with age-related low T?
According to a meta-analysis:
⬆️sexual function
⬇️erectile dysfunction
⛔️No improvement in physical function, depressive symptoms, energy, vitality, cognitionhttps://t.co/VY1aYRMfyD pic.twitter.com/uHXHcV1OrD— Michael Weintraub, MD (@MWeintraubMD) December 23, 2023
One of testosterone’s most well-known roles is in sexual health. It stimulates libido (sex drive), supports erectile function, and aids sperm production within the testes. Men with low testosterone often experience reduced sexual desire, weaker erections, and infertility.
TRT (Testosterone Replacement Therapy) has been shown in multiple clinical studies to improve libido and erectile function in men with documented low testosterone, making it a cornerstone treatment for hypogonadal men experiencing sexual dysfunction.
Mood & Cognitive Function
Testosterone significantly influences mood stability, mental clarity, and cognitive processing. Low testosterone has been linked to symptoms such as irritability, low motivation, depressive feelings, and even cognitive fog or memory difficulties.
A meta-analysis in JAMA Psychiatry found that men with low testosterone were more likely to report symptoms of depression, and those treated with TRT experienced notable improvements in mood and energy levels, particularly in cases of mild depression and low motivation.
Red Blood Cell Production
Testosterone stimulates erythropoiesis (red blood cell production) in the bone marrow, helping to maintain healthy hemoglobin levels and reducing the risk of anemia. This function is why men generally have higher hemoglobin and hematocrit levels than women.
However, during TRT, this effect must be monitored to avoid excessive red blood cell production (polycythemia), which can increase the risk of blood clots if not managed.
Fat Distribution
Testosterone helps regulate fat metabolism and distribution, promoting lean muscle retention while limiting visceral (belly) fat accumulation. Low testosterone levels often lead to an increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen, and are associated with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance.
Maintaining healthy testosterone levels supports a leaner body composition, which is protective against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Testosterone Levels Across the Lifespan
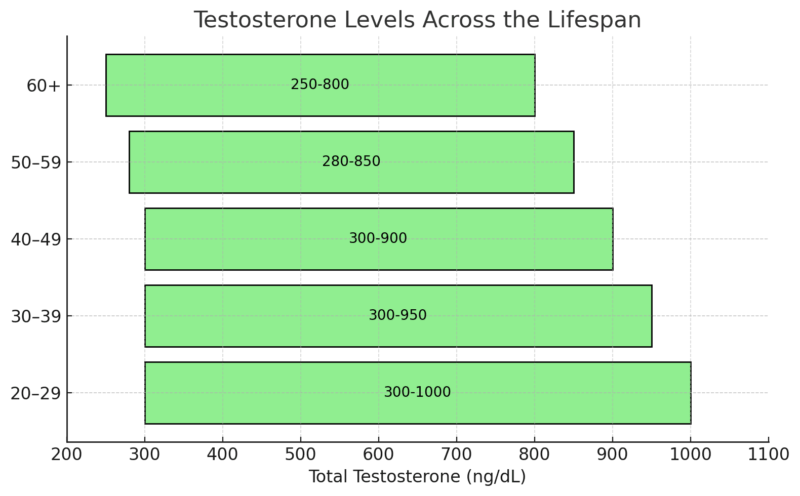
Expanded Explanation
Testosterone levels are highest in the late teenage years and early twenties, aligning with peak physical development and fertility in men. From around age 30, testosterone levels begin to decline at a rate of approximately 1% per year, which is considered a normal part of aging.
This decline can lead to gradual changes in energy levels, libido, mood, and muscle mass. While some reduction is natural, a sharp drop in testosterone may signal hypogonadism, which requires medical evaluation.
It is important to understand that “normal” ranges vary among laboratories and are affected by factors like:
- Time of testing: Levels are highest in the morning (7–10 AM).
- Health conditions: Obesity, chronic illnesses, and medications can lower testosterone.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor sleep, high stress, and lack of exercise can suppress levels.
Monitoring testosterone levels becomes more relevant when symptoms like persistent fatigue, low libido, and loss of muscle mass appear, especially as men enter their 40s and beyond.
Signs of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone (hypogonadism) can present as:
- Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction
- Fatigue and reduced energy
- Loss of muscle mass and increased body fat
- Depressed mood or irritability
- Decreased bone density
- Difficulty concentrating or memory issues
Health Benefits of Healthy Testosterone Levels

Muscle Mass and Strength
Testosterone increases muscle protein synthesis, leading to:
- Greater muscle size
- Improved strength
- Faster recovery post-exercise
Bone Health
Testosterone aids in bone mineral density maintenance, reducing the risk of osteoporosis in men.
Mood and Cognitive Function
Testosterone influences:
- Mood stability
- Energy levels
- Cognitive processing and memory
According to ForHair Clinic, they found that TRT improved depressive symptoms in men with low testosterone, especially in those with mild depression.
Libido and Sexual Health
Testosterone is central to libido, erectile function, and sexual satisfaction.
According to JAMA (2016), TRT significantly improved sexual activity and desire in older men with low testosterone.
Cardiovascular Health (Mixed Evidence)
Healthy testosterone levels are linked with:
However, TRT can increase hematocrit (risk of blood thickening) and may increase cardiovascular risk in some populations, making monitoring essential.
Risks and Concerns with Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
While TRT can help those with medically low testosterone, it is not without risks:
Risk/Concern
Explanation
Polycythemia
Increased red blood cells, raising clot risks.
Sleep Apnea Worsening
It can exacerbate breathing issues during sleep.
Fertility Reduction
Suppresses natural testosterone, reducing sperm production.
Prostate Concerns
Can increase PSA; unclear link with prostate cancer risk.
Fluid Retention
May cause edema in some men.
Natural Ways to Support Testosterone
If you are looking to optimize your testosterone naturally, consider:
- Strength Training: Resistance exercise can increase testosterone.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity lowers testosterone.
- Sleep Quality: Poor sleep lowers testosterone. Aim for 7–8 hours.
- Balanced Diet: Include zinc (oysters, beef), vitamin D (sunlight, fish), and healthy fats.
- Limit Alcohol and Stress: Chronic stress and heavy drinking suppress testosterone.
TRT Should Always Be Medically Supervised
@ashthepharmacist FELLAS 🗣️ Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) for men. I see a lot of videos about HRT for women, but none addressing what happens to men as we age. I discuss how to find out if you’ve low T, what your treatment options are, if they’re safe, and what some side effects are of treatment. I missed one big side effect of the treatment for low T. What was it? #testosterone #trt #menshealth #healthcare #healthtok #medicine #pharmacy ♬ Jazz Hip Hop in the early 90’s(219692) – TOKYO Lonesome Blue
When is TRT appropriate?
TRT can be delivered as:
- Injections (testosterone cypionate/enanthate): Weekly/biweekly
- Gels or creams: Daily application
- Patches: Daily
- Pellets: Implanted every 3–6 months
Related Posts:
- How Much Protein Do You Really Need? Differences…
- 5 Ways Cardio Affects Testosterone, Endurance, and…
- Does Working Out Really Help Slow Down Skin Aging?
- Can a Workout Routine Really Help With Mental and…
- Electrolytes and Energy - What Really Happens in the Body?
- Can You Really Sculpt Your Face with Exercise?