Share Post:
Aging can bring noticeable shifts in muscle mass, metabolism, joint mobility, and energy levels once past 40.
Training smarter instead of harder becomes the secret to maintaining a fit, functional, and energetic body.
Anti-aging workouts are crafted to enhance strength, mobility, and endurance while supporting hormonal balance and cognitive sharpness.
For those seeking a more holistic approach to aging well, Healsend, a modern telehealth platform that offers licensed, doctor-prescribed solutions for weight loss, hormone support, energy restoration, and overall wellness.
Together with exercises, and with consistent effort and proper exercise variety, it is possible to stay lean, agile, and resilient well into later decades.
Let us take a look at the best anti-aging workouts.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Resistance Training with Compound Lifts
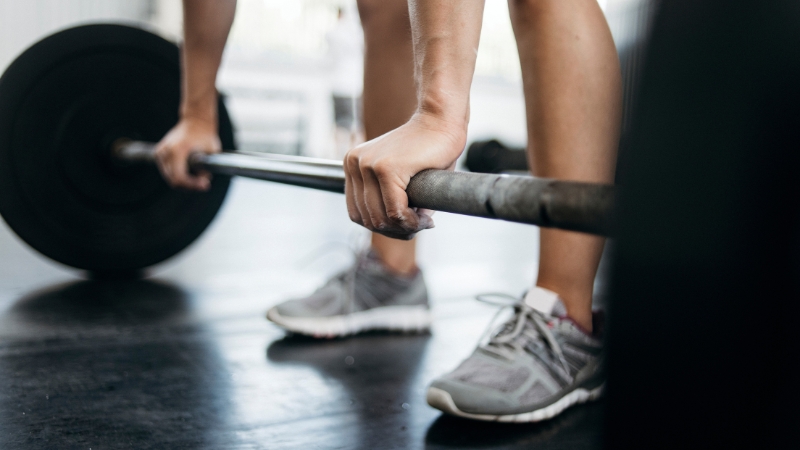

Compound lifts form the backbone of any effective anti-aging fitness routine.
Exercises such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, pull-ups, and rows engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
That full-body stimulation preserves lean muscle tissue, promotes bone density, and combats natural declines in hormone levels that come with age.
Lifting heavy with good form encourages the body to produce more testosterone and growth hormone, both essential for muscle repair and metabolic health.
Beyond appearance, resistance training enhances functional strength, helping carry groceries, climb stairs, or perform other daily movements more easily.
Key Points:
- Boosts metabolism through increased muscle mass
- Strengthens bones, joints, and connective tissues
- Enhances posture and overall stability
- Recommended frequency: 2–3 sessions weekly
2. Functional Core & Stability Training
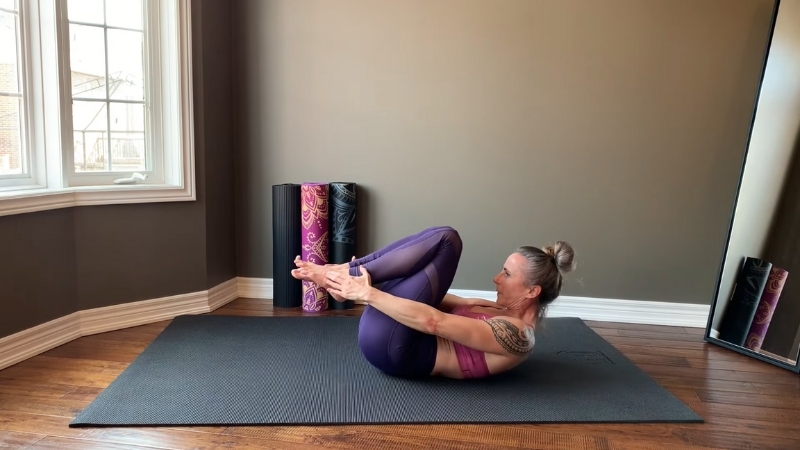

Core stability training is vital after 40, helping reinforce posture, spinal alignment, and coordination.
Movements such as farmer’s carries, planks, Pallof presses, and Bulgarian split squats target deep stabilizing muscles that protect the spine and hips.
Strong core muscles improve balance and reduce the likelihood of injury, especially during daily tasks that require bending, lifting, or reaching.
A resilient midsection supports smoother motion patterns, while also easing tension in the lower back, a common area of discomfort as people age.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced posture and spinal integrity
- Improved body mechanics for everyday tasks
- Reduced lower back pain through stronger stabilizers
3. Zone 2 Cardio
Zone 2 cardio serves as a metabolic reset for individuals over 40.
Activities like brisk walking, cycling, rowing, or light jogging keep the heart rate in a moderate zone, where talking in full sentences remains possible but effort is still noticeable.
Training in this range promotes fat oxidation, enhances mitochondrial function, and supports cardiovascular endurance.
Mitochondria act as the cell’s powerhouses, and improving their efficiency contributes directly to higher energy and better metabolic health.
Key Highlights:
- Strengthens heart and lung capacity
- Improves fat utilization for energy
- Enhances brain performance and focus
- Ideal frequency: 3–5 sessions per week, 45–60 minutes each
4. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
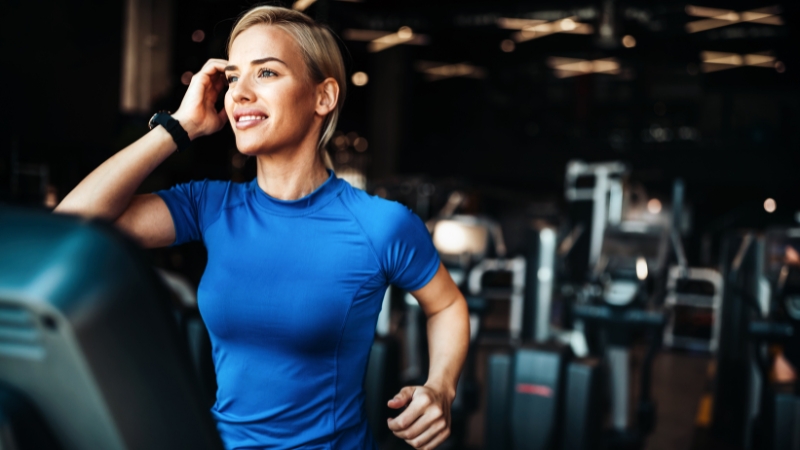

High-Intensity Interval Training focuses on alternating short bursts of maximum effort with brief recovery periods.
Exercises can include sprint intervals, cycling bursts, kettlebell swings, jump squats, or full-body circuits performed in short rounds lasting 20 to 60 seconds, followed by rest or low-intensity recovery.
HIIT sessions stimulate significant calorie burn within a short timeframe, making them ideal for busy individuals over 40 who want to maintain lean muscle mass while promoting fat loss.
The body continues burning calories long after the workout ends due to a phenomenon called excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC).
Improving insulin sensitivity is another core benefit, allowing the body to manage blood sugar levels more effectively.
HIIT also boosts cardiovascular strength, promoting better oxygen delivery to muscles and improving overall stamina.
Advantages:
- Rapid calorie burn with minimal muscle loss
- Increased cardiovascular efficiency
- Improved hormone and metabolic balance
5. Mobility & Flexibility Work
Mobility and flexibility training are often overlooked but remain critical for aging gracefully and maintaining independence.
As years progress, joint cartilage, muscles, and tendons lose elasticity, leading to stiffness and a restricted range of motion.
Mobility work ensures that strength and cardio training can be performed safely and effectively. Improved flexibility decreases the likelihood of injury, muscle tightness, and joint discomfort.
When muscles move smoothly through their full range, each exercise, from squats to lunges, feels more natural and less taxing on the joints.
Integrating these movements daily helps release tension caused by sedentary habits and stress.
A short morning routine of dynamic stretches or an evening yoga session can significantly improve posture, circulation, and recovery after strenuous workouts.
Daily Practice Goals:
- Maintain 10–15 minutes of mobility-focused movement
- Address major joints: hips, shoulders, and spine
- Incorporate foam rolling or yoga sequences regularly
6. Targeted Lower-Body Strength

Lower-body strength anchors physical health after 40.
Exercises like dumbbell or kettlebell front squats, heel-elevated goblet squats, Bulgarian split squats, and barbell hip thrusts stimulate major muscle groups in the legs and glutes.
Strong legs improve balance, stability, and metabolic activity, since larger muscles demand more energy even at rest.
Maintaining lower-body power also supports joint alignment, making daily tasks and athletic activities easier.
Key Benefits:
- Increased lower-body strength and muscle tone
- Enhanced metabolism through large muscle engagement
- Better stability, reducing the risk of falls
7. Balance Training
@fitnesswithadriana_ Replying to @H_carrx Try this approach!😊 #stairmaster #stairmasterworkout #womenover40 #genxwomen #menopause #perimenopausesupport #midlifewomen #womenover50 #bodytransformation #leanmuscle #lowbackpainrelief #cardiochallenge ♬ original sound – Adriana | Menopause Coach
Balance becomes increasingly important after 40 due to natural declines in coordination and sensory response.
Movements like single-leg stands, side planks with hip drops, and Tai Chi drills train the body to respond effectively to shifts in weight and motion.
Good balance minimizes the risk of falls, enhances confidence, and supports everyday movements like:
- Walking
- Climbing stairs
- Lifting objects
Regular balance work also sharpens neuromuscular control, the communication between muscles and the nervous system.
Training Focus:
- Practice 3–5 times weekly
- Combine static and dynamic balance exercises
- Engage stabilizer muscles and improve reflexes
8. Daily Walking

Walking remains one of the simplest and most effective anti-aging exercises.
A daily goal of 7,000 to 10,000 steps promotes circulation, brain health, and emotional well-being.
Light movement throughout the day reduces inflammation, aids digestion, and supports heart function.
Incorporating walking into breaks, social time, or commutes maintains consistent physical activity without requiring a gym.
Regular walking stabilizes weight, improves mood through endorphin release, and helps maintain mobility.
Advantages:
- Strengthens heart and lungs naturally
- Reduces stress and supports better sleep
- Keeps metabolism active through consistent motion
The Bottom Line
Sustained health after 40 relies on smart, consistent effort rather than intensity alone.
Combining resistance work, cardio, flexibility, and balance creates a complete program for longevity and strength.
Proper nutrition, sufficient rest, and stress control further amplify the results, keeping both body and mind in peak condition through every stage of life.
Related Posts:
- Supermodel Cardio Secrets – The Workouts That Keep…
- Top 12 Exercises That Help Women Over 40 Stay Lean…
- Full Body Stretch Routine: 12 Steps I Follow to Keep…
- Should You Lift Weights to Get Lean? What Works for…
- How to Motivate People Who Keep Skipping Workouts
- Top 7 Cardio Workout Models Swear By for a Lean Physique