Share Post:
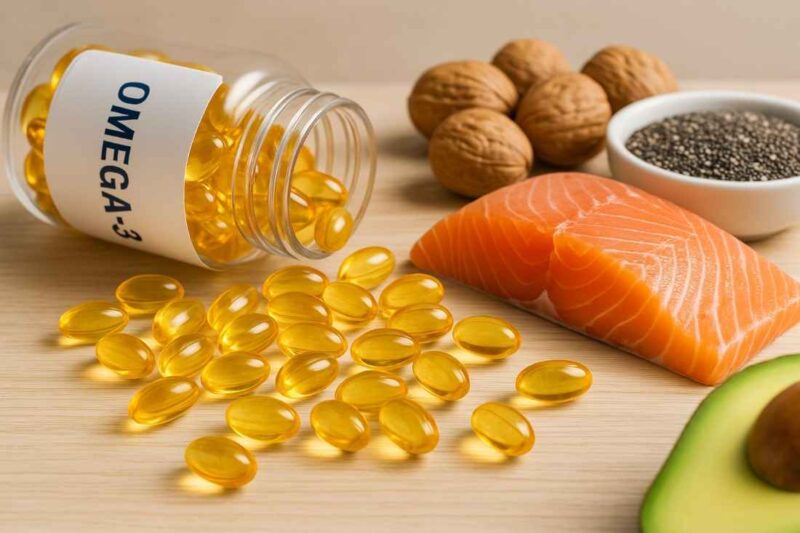
Omega-3 fatty acids play an essential role in maintaining health, especially in those seeking optimal fitness.
These fats—EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)—contribute to various bodily functions, including:
- Cardiovascular
- Neurological
- Metabolic systems
Found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, omega-3s also come from algae, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and plant oils. For those with dietary limitations or preferences, supplements have become a go-to option.
Interest in omega-3 supplements continues to grow as athletes and health-conscious individuals seek efficient ways to support performance, recovery, and long-term wellness.
Omega-3s and Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have become an essential part of conversations around heart health, especially for individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk.
According to research summarized by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), individuals who regularly consume omega-3s may experience a modest reduction in coronary events and deaths related to coronary heart disease.
Although the effects aren’t dramatic, they are consistent enough to justify including omega-3s as part of a comprehensive health strategy.
Food-based sources like salmon, sardines, and mackerel appear to offer greater cardiovascular protection compared to supplements.
Experts suggest that this is due to the broader nutritional matrix found in whole foods. Nutrients found in fish may interact in a way that enhances their collective benefit, something supplements often cannot replicate.
According to insights reported by National Geographic, omega-3s help reduce two major risk factors for heart disease—triglyceride levels and systemic inflammation.
Several heart-related benefits of omega-3s can be summarized in bullet points:
- Triglyceride reduction: Regular omega-3 intake has been shown to lower triglyceride levels, typically by around 15% or more.
- Inflammation control: Anti-inflammatory effects reduce arterial damage and lower the risk of plaque buildup.
- Improved endothelial function: Omega-3s promote better flexibility in blood vessels, allowing them to respond more effectively during exercise or stress.
- Stabilized blood pressure: Regular consumption may contribute to more consistent blood pressure, especially in individuals with hypertension.
- Decreased risk of abnormal heart rhythms: Some evidence suggests omega-3s may reduce the likelihood of arrhythmias.
Consistent intake—particularly through food—supports endurance by maintaining blood vessel health and lowering the physical strain on the heart during exercise.
For individuals focused on performance and longevity, omega-3s deliver tangible cardiovascular support that is difficult to replace.
Immune Function and Cellular Repair

Omega-3 fatty acids enhance immune response through their anti-inflammatory effects and antioxidant properties.
Reduced inflammation helps the body focus on recovery rather than constant immune activation, which can lead to fatigue or overtraining symptoms.
Cellular repair also sees a boost thanks to omega-3 support for mitochondrial health. Efficient mitochondria mean faster recovery, less oxidative damage, and improved resilience after strain.
Athletes often walk the line between progress and breakdown. Faster repair means less time out of training and fewer nagging injuries caused by poor cellular regeneration.
For those aiming to maximize output without compromising health, omega-3s offer multiple layers of protection and recovery support:
- Stronger immune response with reduced baseline inflammation
- Protection against oxidative stress during and after intense training
- Improved mitochondrial efficiency and cellular energy output
- Faster muscle repair and tissue recovery following injury or fatigue
In addition to omega-3 supplementation, some athletes also explore plant-based oils and holistic solutions for broader wellness support.
Brands like Keyoma offer natural products, such as Batana and rosemary oil, that support hair and scalp health, an often-overlooked aspect of self-care for those under physical stress.
Consistent intake of omega-3s—through fatty fish, seeds, or supplementation—can help athletes maintain peak performance without burning out or succumbing to immune-related setbacks.
Anti-inflammatory Benefits for Recovery and Joint Health
Inflammation typically acts as a barrier to recovery and sustained physical performance.
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in managing inflammation levels, offering notable benefits for individuals engaged in regular physical activity and those dealing with joint discomfort due to overuse or degenerative conditions such as arthritis.
By influencing inflammatory pathways, omega-3s can reduce the body’s production of pro-inflammatory compounds like cytokines and prostaglandins.
Faster recovery times lead to more consistent training routines and fewer interruptions caused by pain or fatigue.
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts may find omega-3s particularly helpful during periods of heavy exertion, as inflammation tends to spike with repetitive stress on muscles and joints.
Regular intake can ease symptoms and improve overall comfort, especially in weight-bearing activities or high-impact sports.
To clarify the benefits, key advantages of omega-3s in recovery and joint health include:
- Reduced muscle soreness after intense workouts
- Improved joint flexibility and decreased stiffness
- Lowered swelling around overused or injured joints
- Support for chronic joint issues, such as those caused by arthritis or long-term wear
- Potential reduction in pain medication reliance, as inflammation becomes more manageable naturally
Food-based omega-3 sources, such as salmon, sardines, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts, offer additional anti-inflammatory compounds that work synergistically with EPA and DHA. These foods also provide antioxidants, fiber, and micronutrients that support overall health.
Metabolic & Weight Management Support

Triglyceride reduction ranks high among their metabolic effects.
As noted by the NCCIH, consistent omega-3 intake may reduce triglyceride levels by around 15%.
That change alone can improve cardiovascular health markers and contribute to more stable metabolic profiles, especially in individuals prone to elevated lipid levels.
Fat metabolism and mitochondrial efficiency also benefit from omega-3s. Mitochondria, responsible for converting nutrients into usable energy, perform better when supported by anti-inflammatory fats like EPA and DHA.
That improved function not only helps in day-to-day energy production but also during prolonged physical activity.
Exercise combined with omega-3s creates a synergistic environment in the body, amplifying the effects of physical effort on body composition. Those aiming for long-term weight control may find better outcomes when pairing consistent workouts with a diet rich in omega-3s or smart supplementation.
Outlined below are several ways omega-3s contribute to better metabolic and weight outcomes:
- Reduction in triglyceride levels by about 15%, based on NCCIH data
- Improved fat oxidation and mitochondrial performance
- Enhanced endurance and energy efficiency during workouts
- Potential support for lean muscle preservation in calorie deficits
- Better hormonal response in metabolically stressed states
Those seeking more efficient results during fat loss or athletic training may benefit by making omega-3s a nutritional priority.
Mental and Cognitive Health in Athletes
Cognitive resilience often separates top performers from the rest, especially under pressure. Omega-3 fatty acids, mainly EPA and DHA, support that edge by contributing to mental clarity, emotional control, and stress regulation.
Athletes face frequent cognitive demands—strategic thinking, quick reactions, and emotional discipline—all areas where brain health matters just as much as muscle strength.
Mood regulation and improved focus are two potential benefits seen with omega-3 intake. While scientific findings on supplements and depression are mixed, regular DHA consumption has been associated with delaying age-related cognitive decline, a growing concern even among younger athletes pushing themselves at extreme levels.
Performance isn’t just physical. Mental fatigue, decision-making under stress, and emotional burnout can ruin training consistency. Omega-3s help maintain equilibrium when things get intense.
Key cognitive and psychological benefits associated with omega-3s include:
- Improved focus and mental alertness
- Support for mood balance and emotional control under pressure
- Reduced mental fatigue during prolonged training periods
- Potential delay in cognitive decline with regular DHA intake
Athletes looking for sustained performance mentally and emotionally should give serious attention to omega-3 intake as part of their broader nutrition strategy.
The Bottom Line
Omega-3s offer comprehensive support for physical and mental health, with cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits leading the way. Individuals looking to enhance endurance, resilience, and recovery may find omega-3s a valuable addition to their nutrition strategy.
While food sources deliver the most balanced benefits, supplements still play a role for those with dietary gaps or increased physical demands. Investing in consistent omega-3 intake can support fitness goals and overall wellness alike.
Related Posts:
- Is Aromatherapy Just a Myth or Does Science Support It?
- Does Weight Lifting Make Breasts Sag or Support Them Better?
- 2025's Must-Have Skin Supplements for Youthful and…
- The Truth About Collagen Supplements - Do Pills…
- Can Pre-Workout Supplements Lead to Unwanted Dependence?
- 10 Top Supplements for Faster Recovery After Long Runs