Share Post:
Glutes play a central role in lower body strength, posture, and athletic performance.
Strong glutes improve posture and maintain proper pelvic alignment. Added glute strength supports the lower back and reduces stress on the lumbar spine during loaded movements.
Quadriceps consist of four muscles located at the front of the thigh. Rectus femoris crosses both the hip and knee joints, contributing to hip flexion and knee extension.
Quads control descent in squats and lunges by resisting gravity.
Everyday movements such as climbing stairs, standing up, and sitting down depend on quad strength.
Balanced development of glutes and quads enhances muscular symmetry, improves movement efficiency, and supports long-term lower-body strength.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Hip Thrust
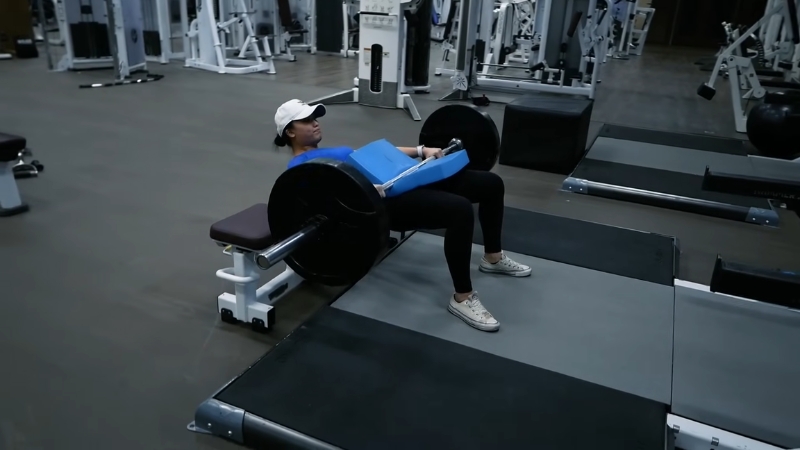

Hip thrust ranks among the most effective exercises for maximizing gluteus maximus activation.
Direct hip extension under load trains the primary function of the glutes while limiting excessive lower back strain.
Upper back rests on a bench, feet stay flat on the floor about hip width apart, and chin remains slightly tucked to maintain a neutral spine.
Driving through the heels lifts the hips until knees, hips, and shoulders form a straight line.
Execution details determine results, especially at lockout. Focus on the following performance cues:
Loading options allow progression across all levels:
Strong hip thrust performance improves sprint acceleration, vertical jump mechanics, and explosive hip power in athletic settings.
2. Squat Variations
Squats recruit all four quadriceps muscles while engaging glutes and core stabilizers.
Movement begins with feet roughly shoulder-width apart, and toes slightly turned outward.
Hips descend while knees track in line with toes.
Different squat variations shift muscular demand. Common options include:
Depth influences muscle recruitment. Greater hip flexion increases glute involvement, while maintaining a vertical torso increases stress on the quadriceps.
Controlled descent enhances eccentric strength and joint stability.
To further develop lower-body endurance and reinforce quad-driven movement patterns outside traditional lifts, Fitness Superstore stair climbers can complement squat training with controlled, stair-based resistance work.
3. Banded Glute Bridge
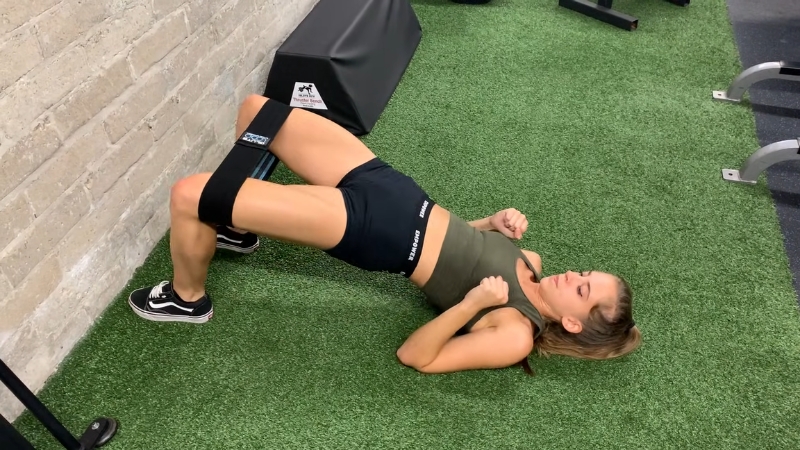

Banded glute bridges create constant tension through the entire range of motion. Position on the floor with knees bent and a resistance band placed above the knees.
Feet remain flat and hip width apart. Pressing knees outward during the lift activates lateral hip stabilizers while the hips extend upward.
Range of motion should remain controlled. At the top, hips fully extend without excessive lumbar arching. Glutes contract firmly before lowering back down with a steady tempo.
Programming can vary based on the training phase.
Effective approaches include:
Continuous outward knee pressure increases gluteus medius contribution and reduces quad dominance during hip extension patterns.
4. Banded Clamshell
Banded clamshell isolates gluteus medius, a muscle critical for pelvic control and knee alignment.
Side-lying position with hips and knees bent creates a stable base. The band sits just above the knees. Feet stay together while the top knee lifts upward without rotating the pelvis backward.
Small details improve effectiveness. Maintain tension on the band even at the bottom of the movement.
Movement should remain slow and controlled rather than explosive.
Strong gluteus medius activation contributes to better lower-body mechanics in compound lifts.
Benefits include:
Consistent practice strengthens lateral hip support and enhances overall movement efficiency.
5. Glute Kickbacks
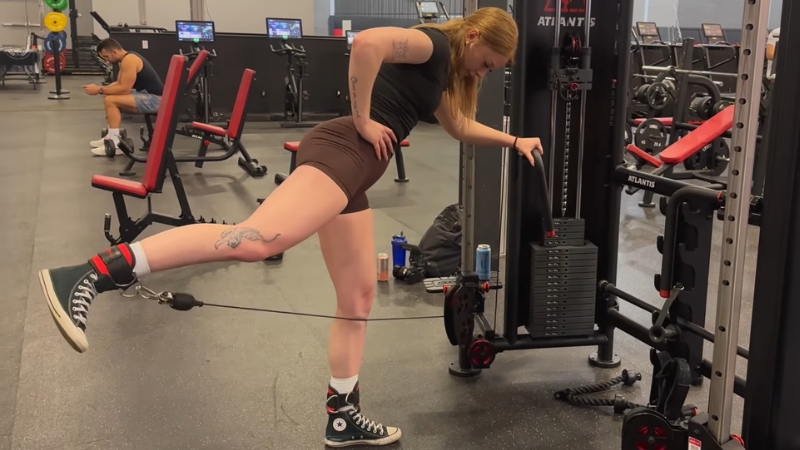

Glute kickbacks isolate hip extension while minimizing quad involvement. Quadruped position places hands under shoulders and knees under hips.
One leg extends backward while maintaining a neutral spine and stable pelvis.
Control defines the effectiveness of this movement. Avoid swinging the leg or arching the lower back.
Instead, focus on squeezing the glute at full extension before returning to the start position.
Progression options expand training stimulus:
Strong contraction at peak extension reinforces proper hip mechanics and strengthens the posterior chain without excessive knee stress.
6. Lunges
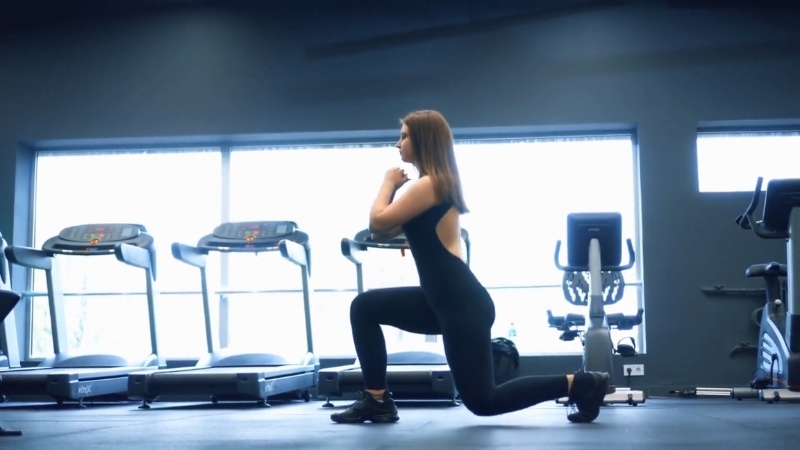

Lunges develop unilateral strength and coordination. Stepping forward, backward, or walking across space challenges balance and lower-body control.
The front knee should track over the midfoot while the torso remains upright.
Different lunge patterns alter joint stress and muscular demand:
Unilateral training addresses strength imbalances between legs and improves athletic performance.
Enhanced balance and coordination transfer directly to running, stair climbing, and directional changes.
7. Bulgarian Split Squats
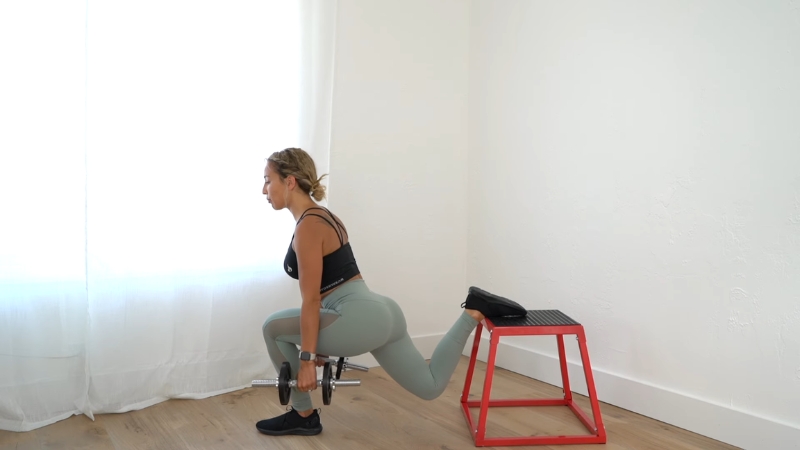

Bulgarian split squats intensify single-leg training by elevating the rear foot on a bench or platform. Front foot stays planted firmly while torso remains upright.
Descending into deep knee flexion increases tension on the front leg quadriceps.
A greater range of motion produces higher muscular demand compared to standard split squats.
Stability also becomes a limiting factor, engaging smaller hip and core stabilizers.
Execution cues improve safety and effectiveness:
Consistent practice corrects side-to-side discrepancies and builds strong, defined thighs with significant quad involvement.
Bonus Exercises to Enhance Glute and Quad Engagement
Curtsy lunges introduce a diagonal stepping pattern that activates outer glutes and inner thighs.
Stepping one leg backward at an angle increases frontal and transverse plane engagement.
Diagonal loading challenges hip stability in ways traditional lunges do not.
Lateral lunges strengthen glutes and quads through side-to-side motion. Shifting body weight into one hip improves adductor flexibility and lateral hip control.
Frontal plane strength contributes to improved cutting and pivoting ability.
Supported single-leg deadlifts reinforce hip hinge mechanics while reducing balance demands.
Holding onto a stable surface allows focus on glute contraction and hamstring tension. Movement trains posterior chain control without excessive spinal loading.
@alivewithzahra Good mornings are a highly effective exercise for strengthening the posterior chain, including the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. By hinging at the hips with a slight bend in the knees, this movement promotes flexibility and stability in the lower back and enhances overall core strength. It’s CRUCIAL to brace your back and core during this exercise to prevent injury and maximize benefits. Engaging these muscles ensures proper form, reduces the risk of strain, and allows for more efficient power transfer throughout the movement. This focus on correct bracing technique not only protects the spine but also helps in building a robust and resilient midsection, which is essential for overall athletic performance and daily functional activities. #StrengthTraining #CoreStrength #BackHealth #ProperForm #FitnessTips #PosteriorChain #FunctionalFitness #Fitness #Gym #GymTok #GymGirl #PersonalTraining ♬ HOW IT GOES – Matt Corman
Good mornings strengthen hip extension through a controlled hinge pattern. Barbell or bodyweight versions require neutral spine alignment and a slight knee bend.
Consistent inclusion of these supplemental movements enhances total lower body development and reinforces balanced muscle activation.
Final Thoughts
Glute-dominant exercises increase hip power and improve overall shape. Quad-focused movements develop leg strength and knee stability.
Effective programming combines compound lifts such as squats, lunges, and split squats with isolation exercises like kickbacks and clamshells.
Unilateral training enhances balance and corrects strength asymmetries.
Consistent training with progressive resistance leads to long-term strength gains and visible lower-body definition.
Related Posts:
- Strength Training for Women - Busting the Bulky Muscle Myth
- Kas Glute Bridge for Beginners - Getting Started
- Resistance Band Arms, Abs, and Booty Workout - 10…
- The 10 Best Bodyweight Back Exercises - The Ultimate Workout
- Top 12 Exercises That Help Women Over 40 Stay Lean…
- 10 Simple Face Exercises That Women Over 40 Follow…