Share Post:
Gym memberships are not the only route to a sculpted physique.
Growing numbers of people now rely on home-based and outdoor routines to stay active and strong.
Demanding physical activities performed outside traditional gyms can deliver impressive results while keeping movement enjoyable and practical.
With that in mind, let us take a look at those physical activities in greater detail.
1. Swimming
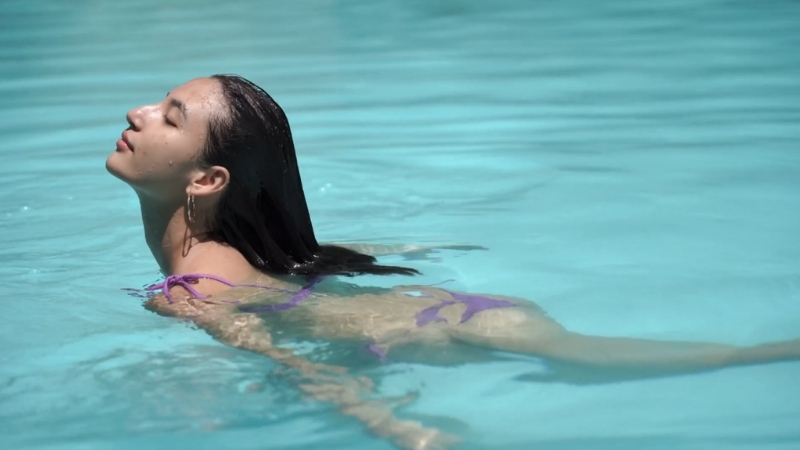

Swimming challenges almost every muscle group while protecting joints through constant water resistance.
Muscles remain active during every phase of movement, creating an effective balance of strength work and cardiovascular conditioning.
Cardio endurance rises steadily as the heart adapts to sustained effort, while muscles gain tone without harsh impact on connective tissue.
Body engagement happens across multiple systems at the same time, which creates visible results with consistent practice and encourages balanced muscular development:
- Core muscles stabilize the torso during rotation and breathing, maintaining alignment in every stroke
- Arms and shoulders generate pulling power through each stroke, driving forward motion
- Legs and glutes provide propulsion and balance, supporting speed and endurance
- Back muscles support posture and spinal alignment, reducing strain and improving efficiency
Low-impact motion reduces stress on knees, hips, and ankles, making swimming suitable for long-term training across age groups.
Controlled breathing patterns increase lung capacity, improve oxygen efficiency, and promote calm mental states during and after sessions.
Sustained effort in water supports fat loss and full-body toning due to continuous resistance applied in every direction.
Different formats offer varied physical and mental challenges, allowing progression without equipment.
Lap swimming builds endurance through repetition, open-water swimming strengthens mental resilience, pool sprints raise intensity, and interval sets provide structured performance gains that keep training adaptable.
2. Trampolining
Trampolining delivers a demanding cardiovascular workout disguised as play.
Continuous bouncing elevates heart rate quickly while forcing the body to stabilize against shifting momentum.
Core muscles stay engaged throughout every jump, which improves balance and spatial awareness over time.
Lower-body muscles manage both impact absorption and force production. Legs and glutes generate lift, while stabilizers maintain alignment during landings.
Joint stress remains low due to the elastic surface, allowing longer sessions without excessive strain or recovery demands.
Repeated bouncing stimulates internal circulation systems and improves muscular endurance over time.
Several physiological effects develop through consistent practice:
- Improved lymphatic flow that supports detoxification
- Increased calorie expenditure through constant motion
- Enhanced agility and neuromuscular coordination
Timed intervals, controlled jumps, and simple stunts raise difficulty levels and keep workouts challenging without additional equipment, making progression easy to manage.
3. Balance and Core Training
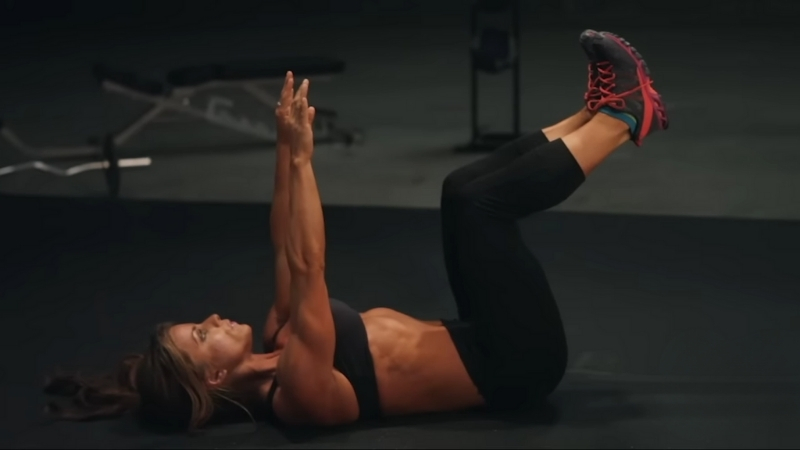

Balance and core training build strength that directly supports posture and daily movement efficiency.
Exercises such as planks, dead bugs, and balance board drills activate deep stabilizing muscles that protect the spine and reduce injury risk during both exercise and routine activity.
Muscle groups work together to maintain alignment during static and dynamic positions.
Abs, obliques, hips, and lower back coordinate to support controlled movement patterns.
Yoga poses like Downward-Facing Dog lengthen the spine, reduce stiffness, and counter long periods of sitting that often weaken postural muscles.
Short sessions deliver noticeable benefits even with limited time.
Blood flow increases, mental focus sharpens, and physical fatigue linked to desk work decreases.
Consistent activation of stabilizers improves posture gradually, while controlled movement enhances flexibility, coordination, and joint awareness.
4. Dance Workouts
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Vanessa Schümmelfeder | Dance Workout (@vanessadanceworkout)
Dance workouts combine cardiovascular conditioning and muscular engagement through rhythmic movement.
Continuous motion keeps heart rate elevated while multiple muscle groups remain active throughout each routine, creating an efficient calorie-burning environment.
Energy expenditure rises naturally as movement intensity increases. Physical benefits develop across several areas during regular practice:
- Legs, hips, and glutes drive most movement patterns and absorb repetitive motion
- Core muscles stabilize turns and directional changes
- Arms contribute to balance and upper-body tone
Flexibility improves through varied ranges of motion, while coordination and rhythm sharpen cognitive focus.
Endorphin release supports mood elevation, and expressive movement builds confidence and body awareness without structured rules or pressure.
Music-driven sessions allow complete freedom of movement without prior experience or structured choreography, making consistency easier to maintain.
5. Lunges and Squats
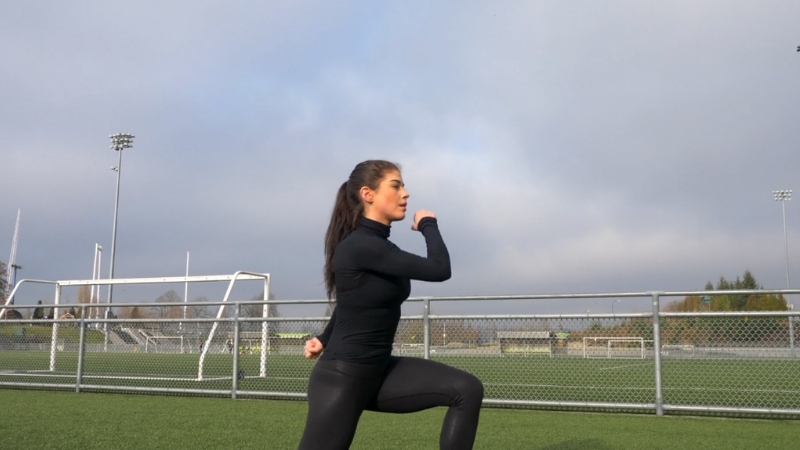

Lunges and squats rank among the most effective bodyweight exercises for lower-body development.
Large muscle groups activate simultaneously, increasing calorie burn while improving strength and muscular endurance.
Controlled movement recruits multiple muscles during each repetition, reinforcing proper mechanics and stability:
- Quads and hamstrings manage knee extension and control
- Glutes generate power and stability during upward motion
- Calves assist balance and propulsion
- Core muscles stabilize the torso throughout each phase
Lunges challenge balance through single-leg loading and improve functional strength used in daily movement.
Squats reinforce efficient movement mechanics and build lower-body power.
Heel raises and circulation-focused movements support blood flow during rest periods.
Added resistance through dumbbells or bands increases intensity as strength improves.
6. Martial Arts or Combat Drills
@vrss_fightgearmartial arts isn’t about toughness. it’s about transformation. not just in the ring, but in who you become outside of it. those brutal rounds, failed reps, and quiet moments where you want to quit? they rewire your brain. they build what psychologists call “psychological hardiness” the ability to stay steady under pressure, in life as well as sport. you don’t just get stronger. you get more grounded. more open. more yourself. fighters in study after study show lower anxiety, stronger self-awareness, deeper connection to others. because when you suffer with people, you grow with them. and that bond stays long after the gloves come off. so when we say “training is my therapy”… it’s not just a feeling. it’s science. it’s truth.
Martial arts training combines explosive force with disciplined control.
High-intensity styles such as kickboxing, karate, and taekwondo elevate heart rate rapidly while strengthening arms, shoulders, core, back, and legs through repeated striking and movement patterns.
Low-impact practices like Tai Chi and Aikido focus on balance, controlled movement, and mental focus.
Shadowboxing provides an effective home-based option that requires no equipment while still delivering cardiovascular and coordination benefits.
Repeated drills sharpen reflexes, improve timing, and enhance body awareness.
Mental clarity improves through focused practice, while fat loss occurs alongside functional strength gains as movement demands vary in speed, direction, and intensity.
7. Climbing
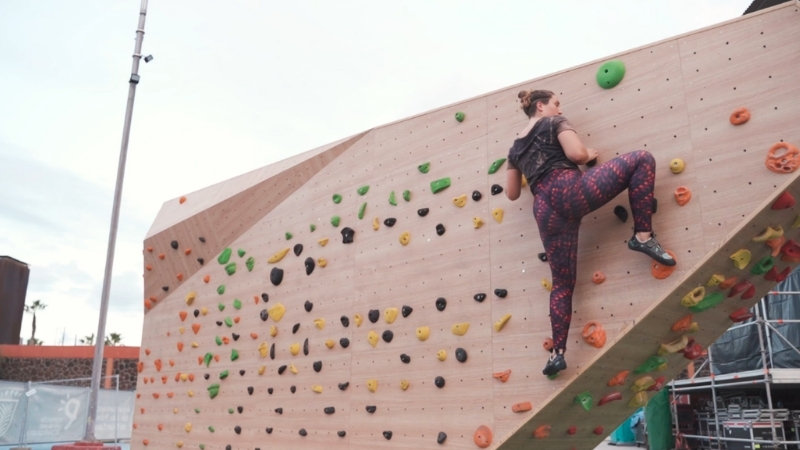

Climbing turns everyday surroundings into resistance training environments.
Multiple muscle groups work together to lift, stabilize, and control body weight during ascent and descent, creating a demanding full-body workout.
Upper and lower body engagement happens simultaneously during each movement:
- Arms and shoulders pull and stabilize the body
- Back muscles support posture and controlled motion
- Legs generate upward force and balance
- Grip strength develops through sustained holds
- Core muscles stabilize movement and alignment
Indoor climbing walls provide structured progression, while outdoor options such as tree climbing or scrambling introduce natural variation.
Parkour-style movement adds vaulting and jumping to challenge coordination and agility.
Grip strength increases rapidly, posture improves through upper-body engagement, and muscular endurance develops through sustained effort.
Mental focus sharpens as problem-solving becomes part of every movement.
The Bottom Line
A sculpted body does not require gym equipment or formal facilities. Consistent movement, creativity, and variety produce measurable physical change.
Each activity above delivers strength, endurance, and conditioning through engaging movement patterns. Water, music, combat, or outdoor challenges provide effective paths to fitness when practiced regularly.
Related Posts:
- Can You Really Sculpt Your Face with Exercise?
- Can a Workout Routine Really Help With Mental and…
- 12 Ways To Feel More Confident In Your Body Without…
- How to Approach Your Gym Crush Without Being Awkward
- Even Small First Results in A Gym that Only You See…
- How Fitness Instructors Can Get More Clients Without…