Share Post:
Muscle recovery is an essential part of any fitness routine. Without proper recovery, soreness, fatigue, and even injuries can hinder progress.
Factors like delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), muscle fatigue, and micro-tears contribute to post-exercise discomfort.
Effective recovery strategies not only improve performance but also enhance overall well-being.
Prioritizing hydration, proper nutrition, rest, and recovery techniques can speed up muscle repair and reduce discomfort.
Hydration & Nutrient Replenishment

Proper hydration and nutrient intake play a key role in muscle function, recovery, and overall performance. Exercise leads to fluid loss through sweat, making it necessary to replenish both water and essential nutrients.
- Water is essential for muscle recovery – It helps transport nutrients, flush out waste, and regulate body temperature.
- Sweat leads to fluid loss – Losing too much water can result in muscle fatigue, dizziness, and reduced performance.
- Aim for at least two liters of water daily – The amount may need to increase based on activity level, temperature, and individual needs.
- Electrolytes help regulate function – Sodium, potassium, and magnesium play a key role in preventing cramps and supporting nerve signals.
- Avoid overhydration – Drinking excessive water without balancing electrolytes can lead to imbalances, causing fatigue or dizziness.
Sources of Hydration
The most effective way to stay hydrated. Sports drinks or coconut water can help replace lost minerals.
Provide hydration while delivering antioxidants and other health benefits. Support fluid balance and offer additional nutrients beneficial for muscle repair.
Post-Workout Nutrition

What you consume after exercise determines how efficiently your muscles recover and rebuild, and incorporating high-quality supplements from VitaminAndSupplements can optimize this process. Nutrient timing and quality make a significant impact on soreness reduction and performance.
- Protein is essential for muscle repair – It helps rebuild fibers damaged during exercise.
- Spread protein intake throughout the day to optimize absorption and growth.
High-quality protein sources include:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef)
- Eggs
- Fish (salmon, tuna, cod)
- Dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese)
- Plant-based proteins (tofu, tempeh, lentils)
Glycogen is the body’s main energy source during workouts, and refueling after exercise ensures sustained energy.
Good carbohydrate sources:
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats)
- Fruits (bananas, berries, oranges)
- Starchy vegetables (sweet potatoes, carrots, beets)
They support muscle recovery and combat oxidative stress caused by intense workouts.
Best antioxidant sources are:
- Tart cherry juice – Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Pomegranates – Packed with polyphenols that aid in muscle recovery.
- Kale – Provides essential vitamins and antioxidants that fight muscle fatigue.
Combining proper hydration with nutrient-dense foods enhances muscle repair, reduces soreness, and improves overall performance.
Active Recovery & Movement
Engaging in low-intensity movement helps muscles recover without adding stress.
Activities such as walking, yoga, and gentle stretching promote circulation and encourage nutrient delivery to damaged tissues. Improved blood flow removes metabolic waste, reducing stiffness and soreness.
A structured cooldown after workouts also prevents excessive tightness. Dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching post-exercise improve flexibility and reduce recovery time.
Engaging in mobility exercises keeps joints and muscles functioning optimally, preventing stiffness.
Active recovery sessions between heavy workout days keep the body in motion without overloading fatigued muscles.
Foam Rolling & Massage
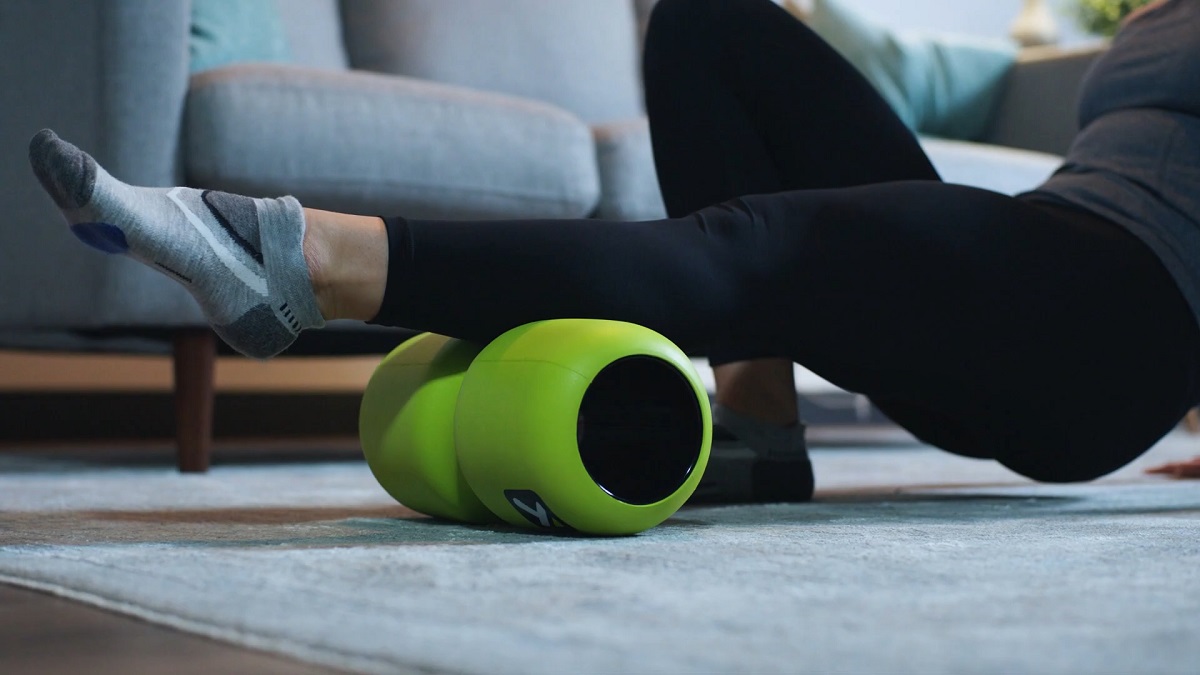

Self-myofascial release techniques like foam rolling alleviate tension and reduce post-exercise soreness.
By applying pressure to tight areas, foam rolling enhances circulation and speeds up recovery. It breaks up knots and adhesions in tissue, allowing for better mobility.
Massage therapy takes muscle recovery a step further by promoting relaxation and reducing inflammation. Professional massages or at-home massage tools like percussive massagers stimulate blood flow, helping to flush out toxins.
Compression garments can further support circulation, minimizing swelling and improving oxygen delivery to recovering muscles. These methods, when used consistently, aid in faster recovery and improved flexibility.
The Ultimate Recovery Tool
Muscle repair occurs primarily during sleep, making it a critical component of post-workout recovery.
During this time, the body undergoes essential processes that restore fibers, replenish energy stores, and regulate hormones.
Proper sleep enhances overall performance, reduces fatigue, and helps prevent injuries.
- Sleep triggers the release of growth hormones, which play a key role in repairing micro-tears in muscle fibers and promoting overall growth.
- Sufficient sleep minimizes inflammation, helping the body recover faster and reducing post-workout soreness.
- Chronic sleep deprivation weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illness and slower recovery.
- Lack of sleep negatively impacts coordination, decision-making, and reaction time, increasing the likelihood of workout-related injuries.
Optimizing Sleep for Recovery
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day supports the body’s natural circadian rhythm, leading to improved sleep quality.
Blue light from electronic devices suppresses melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep. Reducing screen time at least an hour before bed can improve restfulness.
Keeping the bedroom dark, cool, and quiet enhances sleep quality. Blackout curtains, white noise machines, and a comfortable mattress can contribute to better rest.
Short naps (10-30 minutes) can provide an energy boost without interfering with nighttime sleep. Longer naps may be beneficial on particularly demanding training days.
Stress Management & Relaxation Techniques
Mental stress has a direct impact on physical recovery. High levels of stress increase cortisol production, which can slow down muscle repair and make the body more prone to fatigue. Reducing stress helps the body recover more efficiently and improves overall well-being.
- Cortisol regulation – Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can interfere with protein synthesis and muscle growth. Managing stress keeps cortisol levels balanced, allowing for better recovery.
- Improved sleep quality – Relaxation techniques reduce mental tension, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
- Lower inflammation levels – Stress contributes to systemic inflammation, which can prolong muscle soreness and stiffness. Implementing stress-reducing activities can counteract this effect.
Effective Relaxation Techniques

Practicing meditation or guided mindfulness exercises can lower stress hormones and promote relaxation. Even five to ten minutes of mindful breathing can help regulate the nervous system.
Deep breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing, activate the parasympathetic nervous system, encouraging muscle relaxation.
Tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in a systematic way can reduce tension and promote a sense of calm.
Some individuals use CBD oil to help alleviate muscle soreness and support relaxation. It may have anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to overall recovery.
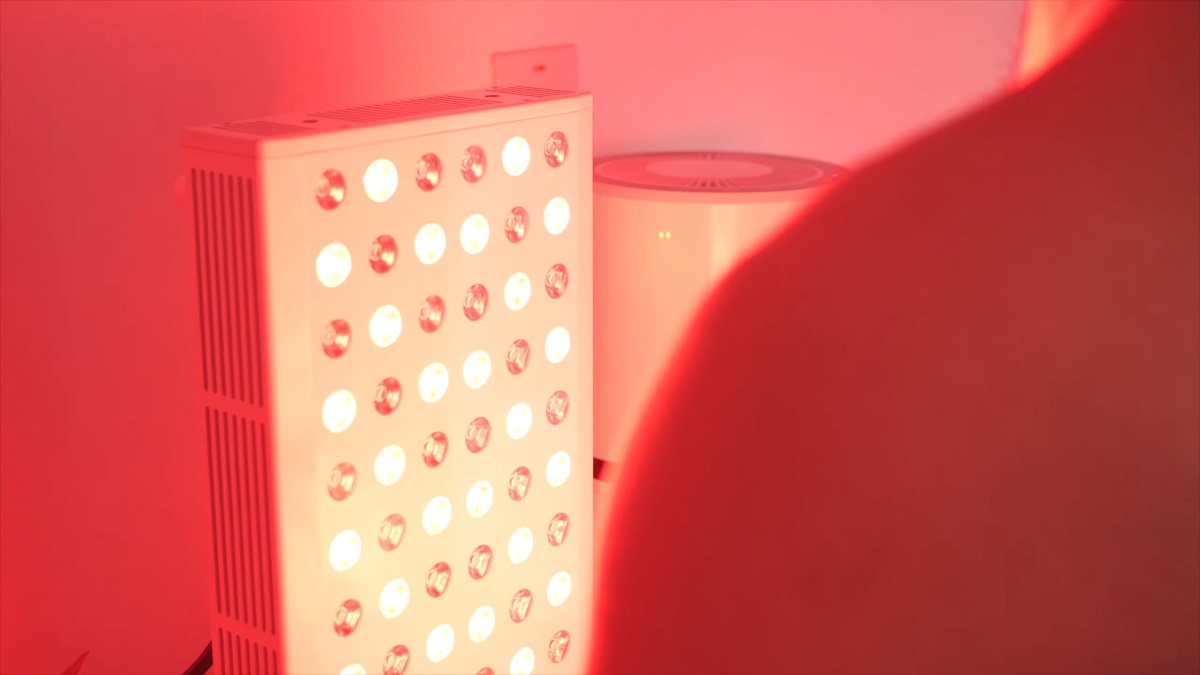
Red light therapy method has been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation and support tissue repair. It works by stimulating cellular activity, which may accelerate healing and improve muscle function.
Cold & Heat Therapy for Recovery
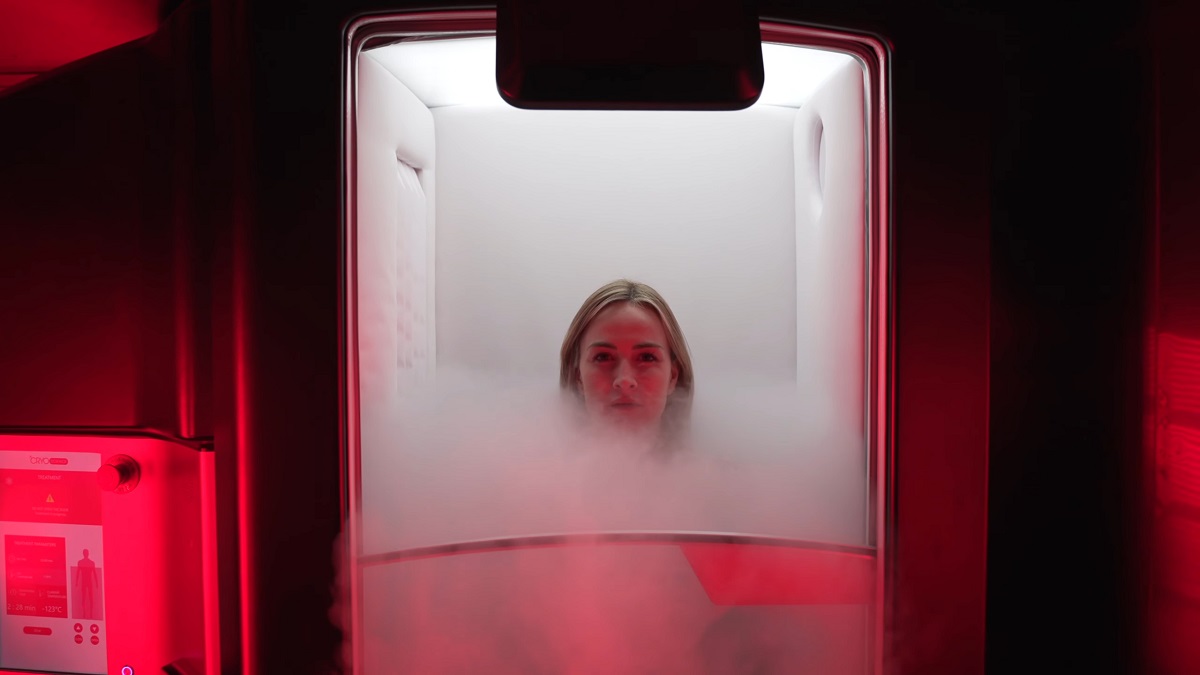

Cold exposure helps minimize post-exercise inflammation and soreness. Ice baths and cryotherapy constrict blood vessels, reducing swelling and preventing excessive muscle damage.
Contrast showers, alternating between hot and cold water, stimulate circulation and promote faster recovery.
Elite athletes frequently use cold therapy to recover from high-intensity training. While ice baths can feel uncomfortable, they significantly reduce pain and stiffness. Short sessions of 10-15 minutes post-workout can improve overall recovery speed.
Heat Therapy (Heating Pads, Hot Showers, Saunas)
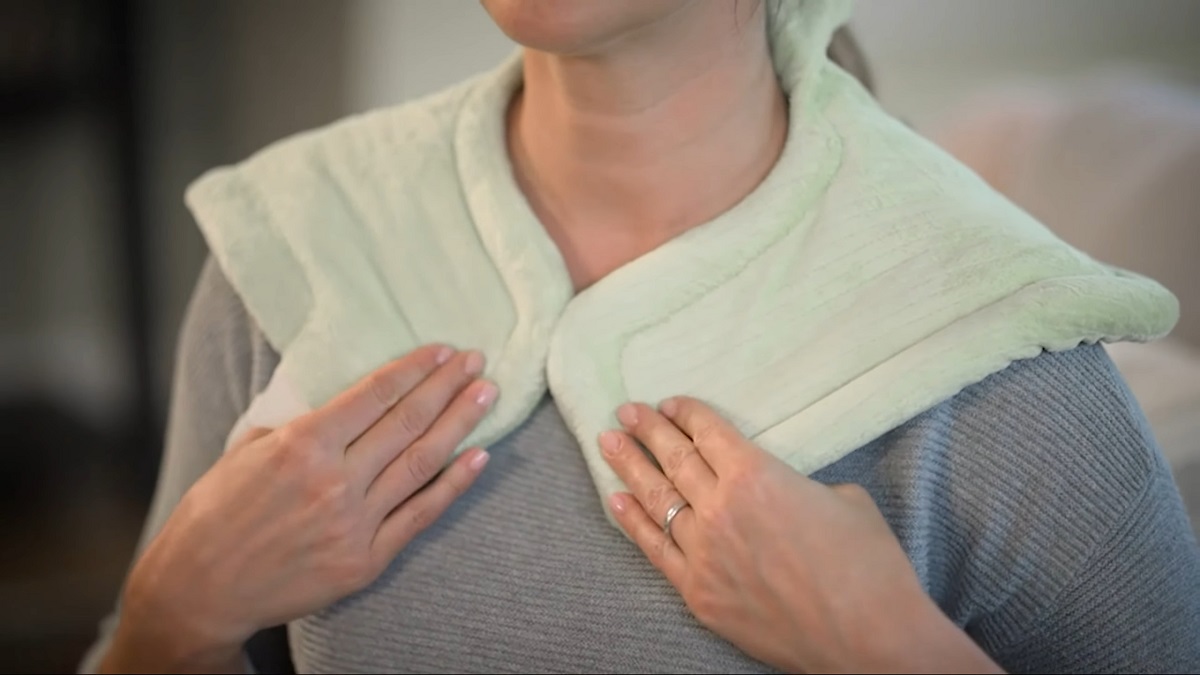

Heat therapy relaxes muscles, increases blood flow, and relieves tension. Heating pads, hot showers, and saunas open up blood vessels, allowing oxygen and nutrients to reach recovering muscles.
This method is particularly useful for alleviating chronic muscle stiffness or tightness.
Applying heat therapy post-workout or before stretching sessions can enhance flexibility and reduce discomfort.
Saunas have also been linked to improved circulation and reduced stress, both of which contribute to better overall recovery.
Supplements & Recovery Aids
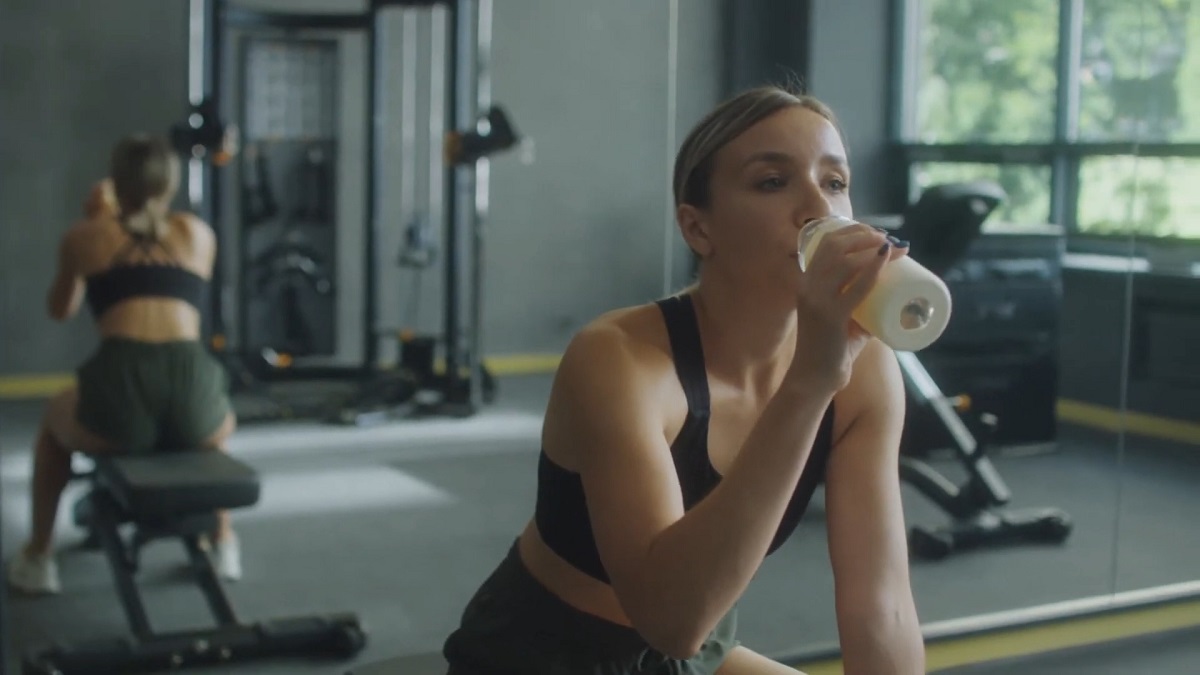

Protein supplements help meet daily protein requirements, especially for individuals with demanding training schedules.
Consuming protein shakes within 60-90 minutes post-workout optimizes muscle repair and replenishes amino acid levels.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are particularly useful for reducing muscle breakdown.
They aid in recovery by providing essential nutrients that the body cannot produce on its own. Supplementing with BCAAs can decrease soreness and enhance muscle endurance.
CBD Oil & Anti-Inflammatory Aids
CBD oil has been recognized for its potential to reduce muscle pain and inflammation. Many athletes incorporate it into their recovery routines to manage soreness.
Magnesium supplements also support muscle relaxation, preventing cramps and stiffness. Ensuring adequate intake of anti-inflammatory nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger can further support recovery efforts.
Recovery-Focused Training Strategies
Overtraining can lead to muscle fatigue, prolonged soreness, and increased injury risk.
Gradually increasing workout intensity allows the body to adapt while minimizing excessive strain. Paying attention to signals like persistent soreness or joint discomfort helps prevent overuse injuries.
Listening to the body and adjusting training intensity accordingly ensures sustainable progress. A well-balanced workout plan includes variation and periods of reduced intensity to support muscle recovery.
Prioritize Rest Days & Active Recovery
Rest days play a significant role in overall performance. Taking one full rest day every 7-10 days allows muscles to repair fully.
Alternating between high and low-intensity workouts prevents excessive strain on the same muscle groups.
On rest days, engaging in light activities like swimming or cycling can improve circulation without placing additional stress on the muscles.
Strategically planning recovery days leads to better long-term fitness results.
The Bottom Line
Muscle recovery is just as important as training.
Hydration, proper nutrition, active recovery, sleep, and strategic rest days all contribute to faster muscle repair. Implementing these recovery hacks can minimize soreness, enhance performance, and prevent injuries.
Prioritizing smart recovery ensures long-term progress and overall well-being.
Related Posts:
- 5 Best Nighttime Habits to Improve Muscle Repair and…
- 5-Minute Fitness Hacks for Women Who Are Always on the Go
- 10 Top Supplements for Faster Recovery After Long Runs
- 4 Best Sleep Positions to Help Sore Muscles Recover Faster
- How to Recover Faster After an Intense Workout
- Is Drinking Raw Eggs a Myth or a True Muscle…